The latest digital transgression is ransomware attack, where hackers attack a system and hold the victim’s data hostage until their ransom demands are met. Otherwise, you risk losing vital data forever. This article covers ransomware and guides you on how to safeguard your data, as well as what to do in case you fall prey to cyber-criminals.
Ransomware definition: What Is Ransomware?

As the name suggests, ransomware is malicious software designed to infect a database and prevent access to users until they pay the ransom through cryptocurrency or credit card.
Types of Ransomeware
Scareware, Screen Lockers, and Encryption Ransomware are some types of ransomware, but encryption malware is the most common attack mode. Ransomware authors encrypt essential data, revoking access to files, databases, or applications. Instructions for payments are shared to get the decryption key.
Although a general practice shows that ransom amount is hardly more than a few thousand dollars at a time, it holds the entire network paralyzed; therefore, major businesses and governmental organizations tend to pay the demands to restore access to their database quickly.
How Does Ransomware Attack Work?
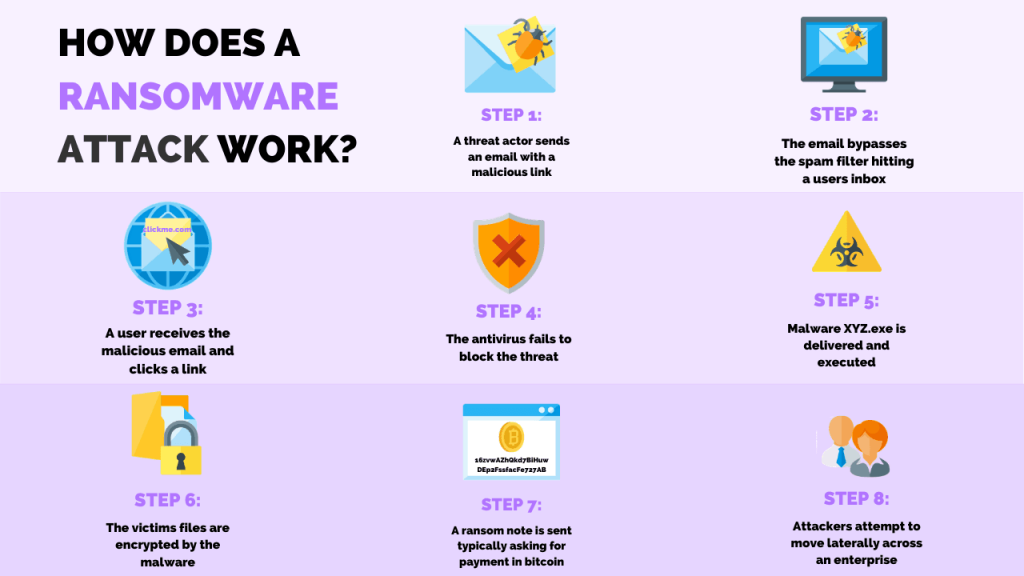
Phishing spam is the most common delivery system where victims download files or attachments that seem trustworthy. Once these files are opened in the target computer, security holes are exploited, or built-in engineering malware tools that prompt administrative access take over the system, and data is encrypted.
How To Prevent Ransomware? – Ransomware Best Practices
A good security practice, in general, ensures your network stays safe from all kinds of malware. You can take the following steps to ensure better protection against attacks like ransomware.
1. BACK-UP:
It is advisable to store data back up on secure cloud servers with high-level encryption and use multiple-factor authentication when handling data on a network. This way, defending against a ransomware attack is as simple as wiping and rebooting your system. Just scan your backup to ensure they are not infected, as ransomware is sometimes programmed to look for network sharing.
2. UP-TO-DATE SOFTWARE:
Software markers in an OS constantly look for updates and keep your system running smoothly. If you run your network on obsolete software, your protection is at risk, and threats are not nullified effectively, making you an easy target for ransomware. In today’s digital world, investing in good security software provides detection and remedial capabilities and ensures long-term protection. It is worth the cost!
3. CREATE SECURITY AWARENESS:
Encourage users to employ stronger passwords and use a two-step, multi-factor authentication to avoid succumbing to malware.
Why Should You Not Consider Paying The Ransom? Or What To Do If You Have A Ransomware Attack?
Law-enforcing authorities advise the victims of ransomware not to pay the ransom. Chances are, you will not get your files back even after paying the ransom, as the cyber-criminals tend to run away after the transactions are confirmed.
However, consult with an IT specialist who may retrieve some encrypted files using certain available software. You can also download security products known for protection against ransomware which may clean the malware from your system at the very least.