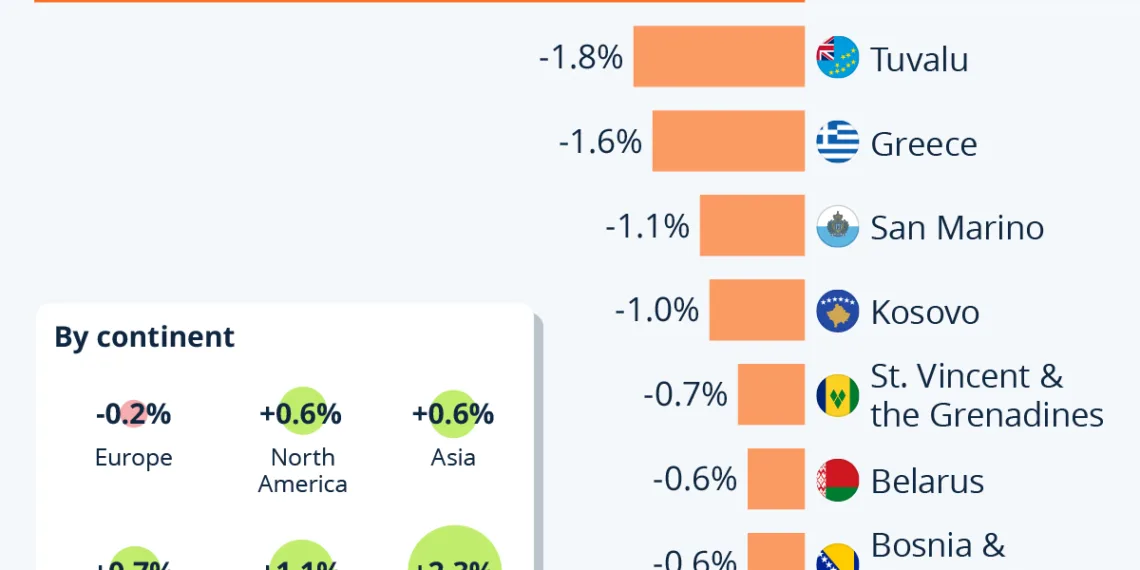
Countries Losing Population Fastest in 2023
In the landscape of global demographics, some countries are witnessing a precipitous decline in their populations. This blog post will delve into the factors contributing to this phenomenon by focusing on countries that are losing their populations the fastest in 2023.
The Impact of Conflict on Population
Ukraine: The Fastest Shrinking Nation
As of 2023, Ukraine has emerged as the nation with the most significant population decline, primarily due to the ongoing conflict instigated by the Russian invasion. The war has spurred a massive exodus of citizens seeking refuge from violence and instability. This situation underlines a critical aspect of demographic changes: conflict can not only lead to immediate casualties but also create a ripple effect, forcing people to flee their homes, destabilizing communities, and altering the nation’s demographics.
Economic Factors and Stagnation
Europe’s Overall Decline
In 2023, Europe is the only continent experiencing a population decline, with a 0.2 percent reduction compared to the previous year. The United Nations Population Division has noted that this decline has been ongoing since 2021. Among the ten countries facing the sharpest population decreases, six hail from Europe. Countries such as Greece, San Marino, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Albania, and Kosovo are significant representatives of this demographic trend.
The Role of Birth Rates and Aging Populations
Greece: A Looming Demographic Crisis
Positioned third on the list of the fastest shrinking nations, Greece faces a worrying demographic outlook. According to national statistics, the country could witness a population collapse, with a projected loss of 1 million residents by 2050. Currently home to about 10 million people, Greece is grappling with a birth rate that plummeted by 30 percent between 2011 and 2021. The combination of socio-economic turmoil, exacerbated by the financial crisis of the 2010s and subsequent austerity measures, has dissuaded young people from starting families or prompted them to seek opportunities abroad.
The Aftermath of Political Turmoil
The Balkans: A Legacy of Conflict
The demographic landscape in the Balkans is similarly affected. Countries like Bosnia, Kosovo, and Albania still bear the scars of conflict following the collapse of communism and the violent wars of the early 1990s. These nations have witnessed a significant outflow of citizens, fostering large diasporas that continue to impact local age structures and economies. The consistent emigration reflects not just the desire for better opportunities elsewhere, but also deep-rooted socio-economic challenges plaguing these nations.
Environmental Challenges and Isolation
Tuvalu: The Cost of Climate Change
Ranked as the second-fastest shrinking country in the world in 2023, Tuvalu presents a unique case in this narrative. With a population of just around 10,000 people, this Pacific island nation is facing the dual challenges of economic limitations and extreme isolation. However, climate change exacerbates the situation, with rising sea levels threatening to render Tuvalu uninhabitable. The urgency of this crisis was highlighted during a prominent speech in 2021 when the foreign minister stood in knee-deep water, symbolizing the nation’s desperate plight.
The Broader Implications of Population Decline
The trends observed in these countries underline a significant narrative concerning global demographics. While conflict, economic stagnation, and environmental challenges are immediate factors, the broader implications for governance, social services, and economic viability cannot be overlooked. Nations grappling with these issues must find strategies to address the causes of population decline, focusing on enhancing economic opportunities, stabilizing regions affected by conflict, and factoring in environmental sustainability.
The data concerning fast-shrinking nations paints a complex picture of global demographic changes; understanding this landscape is essential for policymakers and society as a whole in navigating the implications of these trends.