Understanding U.S. Import Dynamics: A Focus on Mexico, Canada, and China
As the global economy continues to evolve, the relationship between nations is increasingly defined by trade. In this context, the United States maintains significant import ties with its closest neighbors, Mexico and Canada, as well as the economic giant, China. Understanding what the U.S. imports from these countries provides valuable insight into both the economic influence of these nations and the complexities of trade agreements.
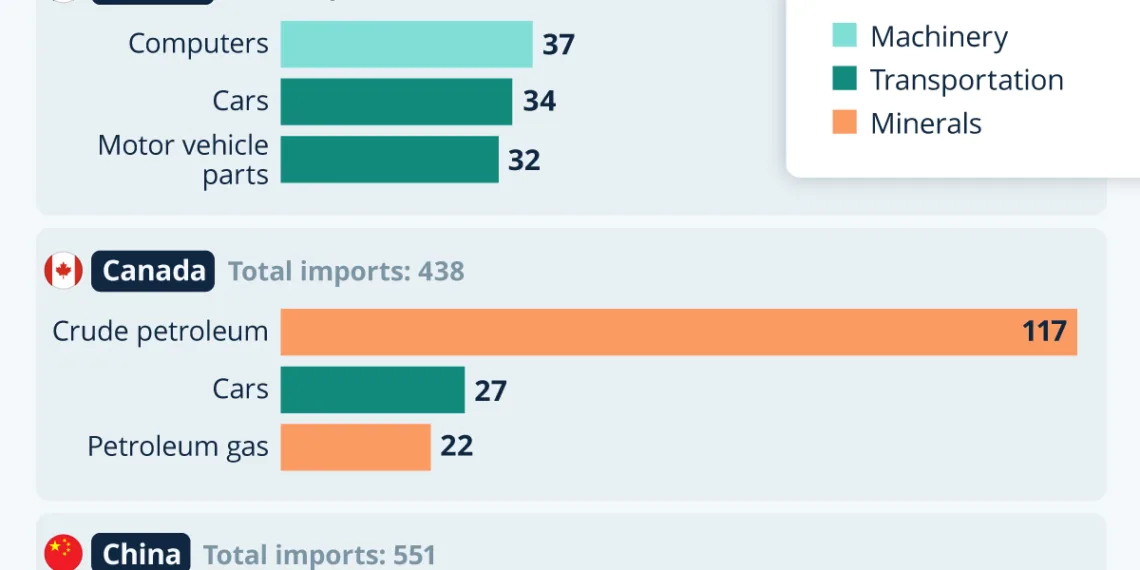
Imports from Mexico
Key Categories
The U.S. imports a diverse range of products from Mexico, with notable categories including:
- Automobiles and Auto Parts: Vehicles are the largest import by value, reflecting the deep integration of the auto industry across North American borders. Major manufacturers like General Motors and Ford source many components and assembly processes from Mexico.
- Machinery: Mexico is also a significant supplier of machinery and computer equipment, contributing to various industries in the U.S.
- Agricultural Products: The agriculture sector sees considerable imports, particularly fruits and vegetables, with Mexico being one of the largest suppliers.
Impact of Increased Tariffs
Recent discussions about potential increases in tariffs have raised concerns among businesses relying on these imports. A proposed 25% duty on goods from Mexico could lead to higher consumer prices and disrupt established supply chains. This threat is particularly pressing for companies that rely on just-in-time manufacturing practices.
Imports from Canada
Major Import Segments
Canada is not only a top trade partner but also a vital source of several key imports:
- Mineral Fuels: Canada is the largest supplier of crude oil to the U.S., highlighting the importance of this relationship to energy security.
- Automotive Products: Like Mexico, Canada is intertwined in the automotive supply chain, providing parts and raw materials for vehicle assembly.
- Wood Products: The lumber trade plays a crucial role, especially in the construction and housing industries.
Tariff Implications
The consideration of imposing tariffs on Canadian goods raises questions about the future of the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA). Any significant changes could unsettle commerce and lead to retaliatory measures from Canada, impacting businesses on both sides of the border.
Imports from China
Dominant Product Categories
China stands as one of the largest exporters to the U.S., with imports heavily concentrated in specific sectors:
- Electronics and Machinery: Products such as computers, telecommunication equipment, and household appliances represent a significant portion of imports.
- Plastic Goods: China also exports a variety of plastic products, which are critical for numerous industries, from manufacturing to retail.
- Miscellaneous Items: This category includes an array of consumer products, indicating China’s vast production capabilities.
Trade War Consequences
The history of tariffs imposed during previous trade disputes has shown a pattern of escalation. If new tariffs were enacted, it could instigate another round of retaliatory tariffs from China, resulting in a direct impact on U.S. exporters. The agricultural sector, in particular, could face severe consequences, as it did during the last trade conflict, where farmers suffered substantial losses.
The Interconnected Nature of Trade
The relationships between the U.S., Mexico, Canada, and China are emblematic of a broader theme in global trade: interconnectedness. The import patterns reflect not just the economic needs of the U.S. but also the geopolitical realities that shape these transactions.
Fentanyl and Immigration Concerns
In addition to economic discussions, political factors also play a crucial role. Issues surrounding the production and trafficking of fentanyl, alongside concerns about illegal immigration, have framed trade negotiations in recent years. The articulation of these concerns highlights that trade policies extend beyond mere economics—they are entwined with national security and social issues.
The Future of U.S. Trade Policy
As the landscape continues to shift with changing administrations and policies, the future of U.S. trade relations with Mexico, Canada, and China remains uncertain. The positions taken by leaders and the subsequent implications for tariffs will significantly influence these countries’ roles in U.S. imports.
This analysis of U.S. imports illustrates the delicate balance of trade relationships, the potential consequences of policy changes, and the intricate ties that bind these nations in the fabric of global commerce.