Overview of Global Arms Exports (2020-2024)
The landscape of global armaments has seen significant shifts from 2020 to 2024, with the United States maintaining its position as the largest exporter of weapons worldwide. This blog delves into the intricate details of arms exports during this period, highlighting the major players, trends, and implications on international relations.
The United States: The Dominant Force
Export Statistics
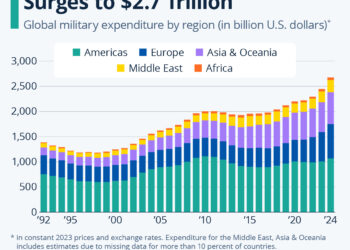
Between 2020 and 2024, the United States emerged as the preeminent arms exporter, supplying weapons to a staggering 107 nations. The U.S. accounted for 43 percent of global arms exports, a notable increase from the 35 percent share recorded between 2015 and 2019. This growth underscores the U.S.’s strategic position in the global arms market, bolstered by its extensive manufacturing capabilities and political ties with numerous countries.
Key Recipients
The primary recipients of U.S. arms during this period reflect a diverse range of geopolitical alliances. Countries in the Middle East, particularly Saudi Arabia and Qatar, were among the top importers, driven by ongoing regional conflicts and security concerns.
France: A Growing Exporter
Rise in Arms Exports
Following the U.S., France claimed the second position in the global arms export market, accounting for 9.6 percent of exports from 2020 to 2024. This marks an increase from 8.6 percent during the previous five-year period. France’s ability to enhance its arms trade highlights its robust defense industry and strategic partnerships, especially within Europe and Africa.
Notable Sales
French arms exports predominantly include advanced military aircraft and naval vessels, catering to the needs of countries seeking to modernize their armed forces.
Russia: A Declining Exporter
Export Decline
Despite being a historical giant in arms exports, Russia’s standing has notably declined from 21 percent of global arms exports between 2015 and 2019 to just 7.8 percent between 2020 and 2024. This downturn reflects several compounding factors, including reduced demand from traditional clients like China and India, who are increasingly producing their own military hardware.
Impact of Political Sanctions
The decline in Russian arms exports can also be attributed to significant trade sanctions from the United States and allied nations, aimed at curbing Russia’s military ambitions and influence. Additionally, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, which began with the full-scale invasion in February 2022, has created substantial pressure on Russia’s military resources, shifting priorities towards domestic arms production rather than export.
Shifts Among Other Exporters
Countries with Decreasing Exports
The arms export market has not been static, with several countries like China, Germany, the United Kingdom, and Israel also experiencing decreases in their export volumes during 2020-2024. Each of these countries faces unique challenges, ranging from tightening domestic budgets to shifts in international demand.
Notable Growth in Exporting Countries
Conversely, countries such as Italy and a few others have successfully increased their arms exports, likely capitalizing on the changing dynamics and high demand for military technology amid global tensions.
The Main Importers of Arms
Top Five Importers
The five largest importers of arms during the 2020-2024 period paint a picture of current geopolitical priorities and conflicts. They are as follows:
- Ukraine – Given the ongoing conflict with Russia, Ukraine’s military needs have surged, leading to significant imports of weapons.
- India – Traditionally one of the largest arms importers, India is transitioning towards self-reliance but still requires substantial imports to modernize its forces.
- Qatar – With aspirations to boost its military capabilities, Qatar’s arms purchases include advanced technology and systems from U.S. manufacturers.
- Saudi Arabia – A key player in regional conflicts, its military modernization programs continue to drive arms imports.
- Pakistan – Pakistan remains reliant on military imports amid tense relationships with neighboring countries.
Conclusion
As we observe these trends in arms exports, the geopolitical landscape continues to evolve. The complex dynamics of international relations play a crucial role in shaping both supply and demand in the global arms market. Understanding these shifts not only provides insights into military capabilities but also reflects broader strategic interests among nations.