The Urgent Threats to Global Biodiversity
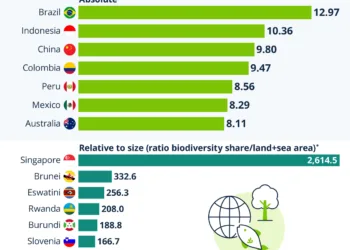
Biodiversity is critical for maintaining healthy ecosystems and ensuring the survival of diverse species. However, recent data reveals alarming trends regarding the various threats that jeopardize biodiversity worldwide. According to the World Database of Key Biodiversity Areas, agriculture and aquaculture pose the largest single threat to these vital regions. Understanding these threats is essential for conservation efforts and sustainable practices.
Agriculture and Aquaculture: The Primary Culprits
Agriculture and aquaculture are major drivers of habitat destruction and species endangerment. The expansion of farmland often leads to deforestation, soil erosion, and the loss of natural habitats for countless species. Additionally, intensive farming practices contribute to pollution and the depletion of natural resources.
Key Issues:
- Deforestation: Clearing forests for crops or livestock reduces habitat for many species.
- Chemical Use: Pesticides and fertilizers can contaminate nearby ecosystems and harm non-target species.
- Overfishing: Aquaculture can deplete fish populations and disrupt marine ecosystems.
Human Intrusions and Disturbance
Human activities have a profound impact on biodiversity. The category labeled "Human Intrusions and Disturbance" captures a range of actions from recreational activities to significant societal unrest. These disturbances alter habitats and can lead to decreased wildlife populations.
Key Factors:
- Recreational Activities: Hiking, camping, and other outdoor activities can disrupt wildlife and lead to habitat degradation.
- Military Activities: Wars and military exercises often result in environmental destruction and long-term ecological damage.
- Urban Development: The expansion of cities into rural and natural areas further encroaches on wildlife habitats.
Biological Resource Use
The utilization of biological resources, whether for sustenance or commerce, poses significant risks to biodiversity. Activities such as hunting, logging, and wood harvesting directly impact species survival and habitat integrity.
Key Considerations:
- Hunting: Unsustainable hunting practices can lead to population decline and local extinctions.
- Logging: Deforestation for timber reduces habitat availability for various species and disrupts ecosystems.
- Illegal Trade: Poaching and illegal wildlife trade threaten endangered species and contribute to population declines.
Natural System Modifications
Human-induced modifications to natural systems can lead to drastic changes in ecosystems. Building infrastructure—such as dams, roads, and urban areas—alters water flow, habitat availability, and ecological balance.
Major Concerns:
- Dams: Construction can flood vast areas, displacing species and disrupting aquatic ecosystems.
- Land Reclamation: Converting wetlands for agriculture or urban use removes crucial habitats for many species.
- Water Diversion: Redirecting water for agriculture or cities can diminish wetland areas, impacting biodiversity.
Pollution: A Global Crisis
Pollution remains a pervasive threat to biodiversity, affecting air, water, and soil quality. Various types of pollution compromise ecosystems and the species that inhabit them.
Types of Pollution:
- Sewage: Untreated waste can contaminate waterways, harming aquatic life.
- Oil Spills: These incidents lead to devastating effects on marine environments and species.
- Acid Rain: Resulting from industrial emissions, acid rain can alter soil chemistry and affect plant and animal life.
Energy Production, Mining, and Transportation Corridors
While categorized under "Other" in terms of ranking, energy production, mining, and transportation corridors significantly threaten biodiversity by altering landscapes and ecosystems.
Impact Analysis:
- Mining: Extractive industries often lead to habitat destruction and landscape degradation.
- Energy Projects: The establishment of power lines and substations can fragment habitats and disrupt animal migrations.
- Transportation Corridors: Roads and railways can create barriers for wildlife, leading to population isolation and increased mortality rates.
Global Action and Collaborative Efforts
Recognizing these threats is the first step towards effective conservation. The upcoming UN Biodiversity Conference COP16, scheduled at the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in Rome, aims to address these challenges. Key discussions will focus on mobilizing resources, crafting monitoring frameworks, and establishing financial mechanisms to protect biodiversity.
Points of Discussion:
- Resource Mobilization: Ensuring funding for conservation initiatives will be critical.
- Monitoring Frameworks: Establishing metrics to assess biodiversity health and threat levels is essential for informed decision-making.
- Financial Mechanisms: Creating sustainable funding sources to support ongoing conservation efforts will help mitigate risks to biodiversity.
By understanding and addressing these threats, we can work collaboratively to preserve the rich tapestry of life on Earth for future generations.