India’s Trade Deficit: An Overview
India’s economy has faced challenges in recent years, one of the most pressing being its persistent trade deficit. Understanding the dynamics of India’s exports, particularly in the context of services and goods, is essential to grasping the nation’s fiscal health and future prospects.
The Current State of India’s Trade Deficit
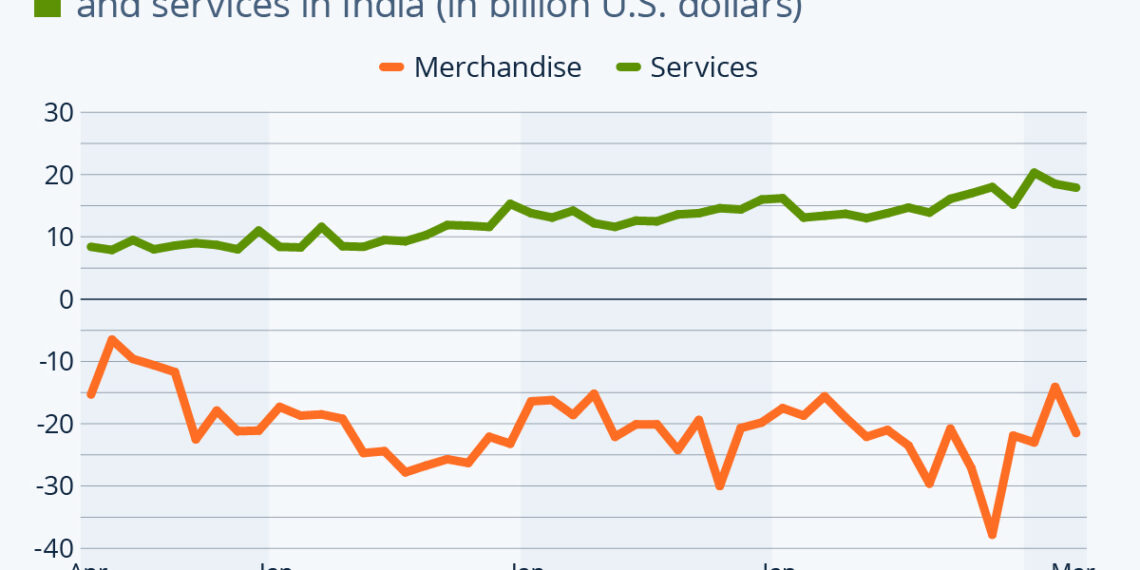
India’s trade deficit has been a significant concern, showing a worrying trend of widening in recent months. As of March 2024, the merchandise trade deficit was recorded at $21.5 billion, a notable recovery from $37.8 billion in November of the previous year. However, it remains considerably higher than the same period in 2023, where the deficit was only $15.6 billion.
Fluctuations in Merchandise Exports
The landscape of Indian merchandise exports has been quite volatile in 2024. Several factors have contributed to this downward trend, including global economic conditions, domestic production challenges, and competition from other nations.
- Weakness in Exports: Indian merchandise exports have shown exceptional weakness, indicating the need for strategic revisions in production and export policies.
- Global Market Competitiveness: As the U.S.-China trade war continues to reshape global trade dynamics, countries like Vietnam and Bangladesh are seeking to bolster their exports to the United States, further complicating India’s position in this competitive landscape.
Services: The Silver Lining in India’s Exports
Despite the ongoing struggles in merchandise exports, services have emerged as a noteworthy sector for India, showcasing a growing trade surplus. This divergence highlights the potential strengths within India’s economy that could be leveraged for future stability and growth.
Services Export Surplus
India’s services sector has flourished, providing a counterbalance to the losses seen in goods exports.
- IT and Software Services: With a robust IT industry, India has become a global leader in software services, contributing significantly to the surplus.
- Hospitality and Tourism: Growth in tourism and hospitality services has also been a boon, attracting international visitors and investment.
The Impact of Global Trade Dynamics
The ongoing U.S.-China trade tensions have presented both challenges and opportunities for India. While some countries are positioning themselves as alternatives to Chinese goods, India faces hurdles due to inadequate domestic manufacturing infrastructure.
Manufacturing Limitations
- Lack of Export Strength: Unlike some of its Asian counterparts, India’s manufacturing capabilities have not sufficiently developed to allow it to take advantage of the shifting trade dynamics.
- Strategic Initiatives Required: To improve its competitive stance, India needs to invest in its manufacturing sector, focusing on efficiency, quality, and export readiness.
Conclusion: An Overview of Key Takeaways
India’s trade landscape is characterized by significant challenges, particularly regarding merchandise exports, while the services sector continues to provide a glimmer of hope amid a trading deficit. The country must strategically enhance its manufacturing capabilities to fully leverage its potential in the evolving global trade arena. The emphasis on services exports could be a critical factor in balancing the trade deficit, shaping India’s economic future in an interconnected world.