The Global State of Waste Management: An Overview
The management of solid waste is a significant concern worldwide, as it plays a crucial role in environmental sustainability and public health. Despite advances in waste management technologies, many regions still struggle with the effective handling of household and commercial waste. This blog delves into the current state of waste management across the globe, emphasizing key statistics, challenges, and best practices.
The Disparity in Waste Management Practices
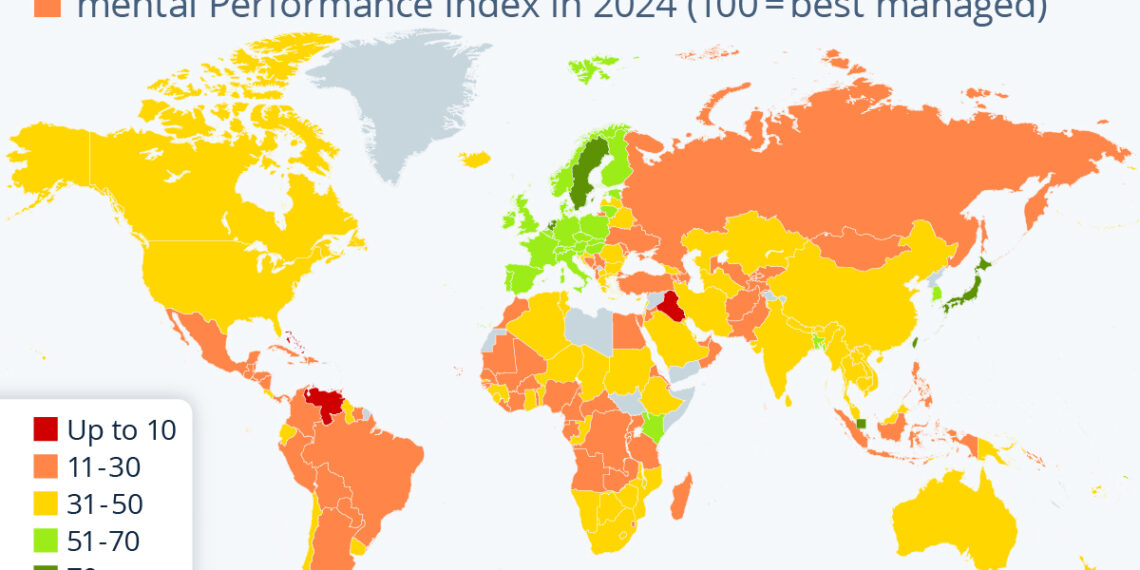
Waste management practices vary dramatically across different regions, highlighting a clear disparity in how countries approach the issue. According to the Yale Environmental Performance Index, certain areas consistently score lower in waste management effectiveness. Caribbean nations, along with some countries in Central Asia, Eastern Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, often find themselves at the bottom of the rankings. Notably, island nations face unique challenges due to their limited land for waste disposal, amplifying their waste management dilemmas.
Challenges Faced by Island Nations
Island nations typically have higher population densities and limited space, which complicates waste management efforts. The constraints of geography lead to a reliance on landfills and incineration, which can result in severe environmental consequences. Additionally, the costs of transporting waste off the islands can be prohibitive, leading to inadequate waste processing solutions.
Future Projections in Waste Generation
The World Bank has conducted research indicating that waste generation is expected to increase rapidly in regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia by 2050. This growth is primarily driven by rising populations and expanding access to modern consumer markets. While East Asia-Pacific currently generates the most waste globally, its growth rate is expected to be slower than that of emerging economies.
Implications for Waste Management
The anticipated rise in waste production presents significant challenges for safe waste management. As nations work to develop their waste management systems, they must also contend with the effects of poor waste disposal practices, which can lead to widespread environmental contamination. These challenges could potentially overwhelm existing infrastructure if not addressed in a timely manner.
The Environmental Impact of Poor Waste Management
A significant concern associated with improper waste management is its contribution to greenhouse gas emissions. According to recent findings, solid waste is responsible for 5 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, factors like leaching, burning, and pest infestation from poorly managed waste can lead to soil, water, and air contamination.
The Threat of Plastic Waste
Plastic pollution is one of the most pressing environmental issues linked to waste management inefficiencies. Plastic waste often finds its way into oceans, posing a severe threat to marine ecosystems. This pollution can harm wildlife and disrupt the balance of marine habitats, showcasing the urgent need for effective waste management strategies globally.
Global Leaders in Waste Management
Despite the challenges faced by many countries, there are notable examples of effective waste management practices. Singapore, Taiwan, Japan, the Netherlands, and Sweden are recognized as global leaders in this arena, achieving high scores on performance indices related to waste management. Their success can be attributed to comprehensive policies, innovative technologies, and public awareness campaigns that encourage sustainable waste disposal practices.
The Role of Scandinavian and German-Speaking Countries
Countries in Scandinavia and the German-speaking world, along with the United Kingdom, have also made notable progress in waste management. These nations frequently implement rigorous recycling programs, invest in waste-to-energy technologies, and prioritize sustainability in urban planning, all of which contribute to their high rankings.
Global Waste Management Rankings
Examining global waste management rankings reveals disparities in performance among various nations. For instance, Australia ranks 35th, while the United States falls even lower at 47th. These rankings reflect the broader trends in waste management and underscore the ongoing need for improvement in many developed countries.
Conclusion
The state of waste management globally is a complex and evolving issue. As waste generation continues to rise and environmental challenges mount, the urgency for effective and sustainable waste management solutions becomes increasingly critical.