Data Center Energy Consumption Surges Amid AI Boom
The rapid adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) is set to transform various sectors, including the energy market. According to a recent report from the International Energy Agency (IEA), global electricity demand from data centers is expected to more than double in the next five years, propelled primarily by this technological boom. This surge in energy consumption poses significant questions about sustainability and the environmental impact of data centers, as they continue to become critical in processing AI workloads.
Rising Demand for Electricity in Data Centers
The Factors Driving Demand
The massive growth in AI applications is a primary driver of increased electricity demand in data centers. As organizations optimize operations and enable innovative applications through AI, the energy required to process this data has skyrocketed. This trend indicates that data centers will become one of the largest consumers of electricity globally, raising concerns about energy sustainability.
Predictions for the Next Decade
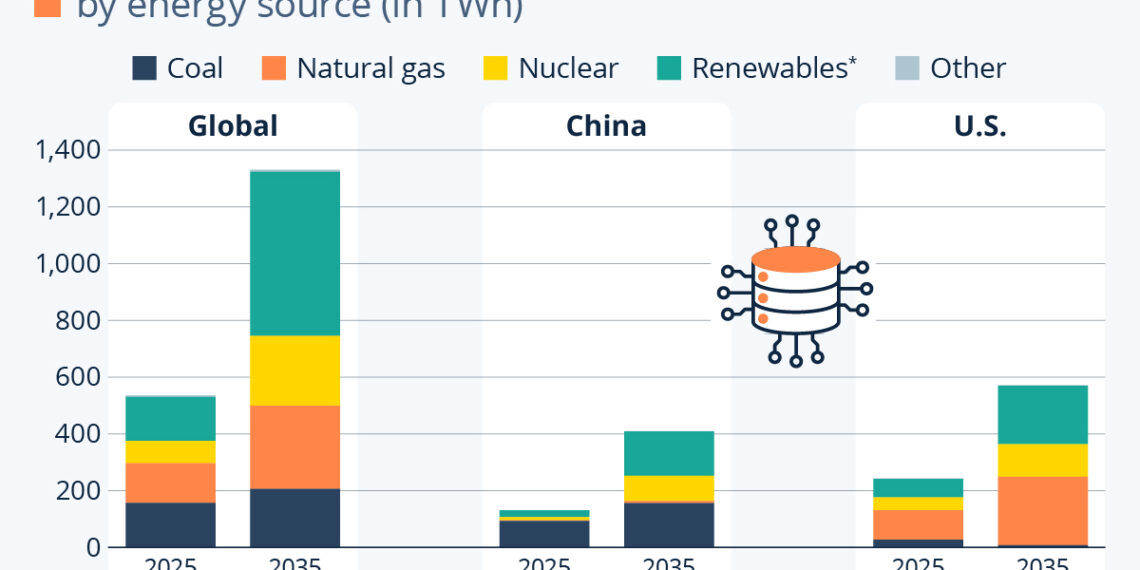
By the end of the decade, around 50% of global energy demand for data centers is anticipated to come from renewable sources such as solar PV, wind, and hydroelectric power. This shift could mark a significant change in how data centers operate and their impact on global energy consumption. The IEA notes that these renewables will emerge as the fastest-growing source of electricity for data centers, reshaping the energy landscape.
Energy Sources and Their Global Distribution
Diverse Energy Mix
To meet the electricity demands of data centers, a varied mix of energy sources will be required. The specific sources depend significantly on local market conditions, including availability and cost. For instance, in China, coal remains a dominant source of energy, while the United States leans more towards natural gas. As the world adapts to meet rising energy demands, the composition of energy sources will continually evolve.
Future Projections for Different Regions
In terms of renewable energy, significant advancements are expected. In China, solar PV electricity generation is projected to increase dramatically from 7 TWh in 2025 to 83 TWh by 2035. This growth will approach the anticipated U.S. output of 97 TWh by 2035. Wind power generation will also see notable increases, with the U.S. expected to expand from 28 TWh to 83 TWh, compared to China’s projected 44 TWh by the same year.
Regional Impact on Electricity Demand
Disparities Among Countries
The report outlines that the impact of increased electricity demand will not be uniform globally. In the United States, data centers could account for nearly half of the growth in electricity demand. This trend is even more pronounced in Japan, where data centers are projected to be responsible for more than half of the electricity demand growth. Countries like Malaysia are expected to experience a more moderate impact, with data centers contributing to approximately one-fifth of the growth.
Environmental Concerns
The rising demand for electricity in data centers raises pressing questions regarding environmental sustainability. Currently, data centers contribute around 180 megatons of indirect CO2 emissions due to electricity consumption, representing approximately 0.5 percent of total combustion emissions globally. The dual role of AI, which requires substantial energy to function but can also enhance efficiency, complicates this narrative.
The Role of AI in Optimizing Energy Use
Balancing Energy Consumption and Efficiency
The dual nature of AI presents both challenges and solutions regarding energy consumption. While the operation of data centers inherently generates emissions due to increased electricity use, AI technology has the potential to enhance operational efficiency. By optimizing systems and accelerating advancements in energy technologies, such as renewable energy and battery storage, AI may help mitigate some negative environmental impacts.
Insights from Industry Leaders
Fatih Birol, the IEA Executive Director, emphasized the crucial role AI plays in the current energy landscape, stating, “With the rise of AI, the energy sector is at the forefront of one of the most important technological revolutions of our time.” He underscored the responsibility of societies, governments, and companies in shaping how this technology is utilized for the greater good.
Conclusion: A Complex Future Ahead
While the provided insights focus on the energy demands of data centers in light of AI advancements, the full impact on the environment and energy policies remains to be fully understood. As companies and nations navigate this new technological frontier, the blend of energy generation and AI usage will be critical in determining the sustainable future of data centers. The IEA’s report serves as a vital reference point in understanding this evolving relationship between AI and energy consumption.