The Rise of Chrome: A Revolutionary Shift in Browsing Experience
Introduction to Chrome’s Market Entry
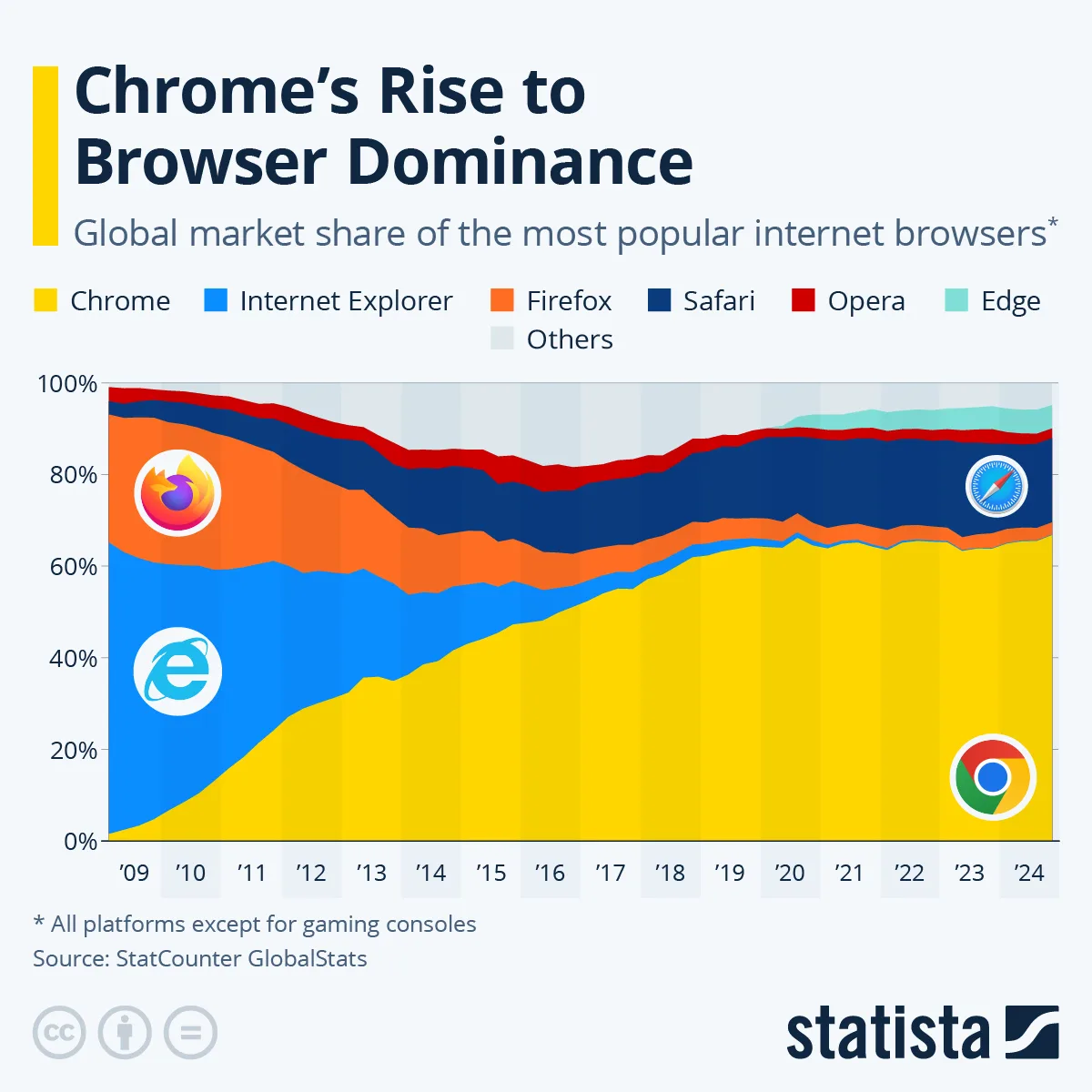
The landscape of web browsing shifted dramatically when Google introduced Chrome on September 2, 2008. Contrary to the doubts surrounding this launch, it quickly became apparent that Google’s entry into web browsers was long overdue. The company had primarily relied on browsers to facilitate access to its core services, particularly Google Search. Therefore, launching a browser ultimately made strategic sense to enhance user experience and secure more control over web interaction.
The Background Leading to Chrome’s Development
Google’s Strategic Decisions
Before the advent of Chrome, Google’s CEO, Eric Schmidt, had been contemplating the development of a web browser for years. However, he believed that the company wasn’t ready to engage in the so-called “browser wars,” a highly competitive market dominated by Internet Explorer, which was then a part of Microsoft’s offerings. By the time Chrome was readied for release, Google had already evolved into a multi-billion-dollar powerhouse, providing a solid foundation to challenge Microsoft’s stronghold.
The Product Launch
The official release of Chrome marked a significant technological milestone. Unlike existing browsers, Chrome was designed with speed, simplicity, and security in mind. Its open-source component allowed for broader community involvement, fostering rapid innovation and improvements. Within a year, Chrome was making waves, and by 2012, it had surpassed Internet Explorer to become the world’s leading browser, redefining user expectations and prompting other companies to enhance their offerings.
Chrome’s Ascent to Dominance
Rapid Adoption and User Engagement
Chrome’s user interface was minimally cluttered, making it appealing, especially to users who prioritized efficiency. Moreover, its seamless integration with Google services like Gmail, YouTube, and Drive provided an excellent user-centric approach, encouraging users to adopt Chrome as their primary browser. According to statistics from StatCounter, by 2023, Chrome commanded a staggering market share of approximately 65%, which is more than three times that of its nearest rival, Safari.
The Influence of Open-Source Development
One of Chromes’s key advantages has been its open-source project, Chromium. This foundation has allowed developers from around the world to contribute to its functionality and security, leading to a more robust product. As a result, Chrome has consistently released updates to ensure high performance and user satisfaction, incorporating features that cater to evolving browsing requirements.
Current Landscape and Antitrust Concerns
The Antitrust Ruling
Despite its success, Google has faced significant scrutiny from regulatory entities, particularly concerning its dominance over online searches and digital advertising. A landmark antitrust ruling in August 2023 concluded that Google maintained an unlawful monopoly, leading to increased pressure on the tech giant.
Proposed Remedies from the DOJ
In response to these findings, the U.S. Department of Justice proposed a series of remedial actions, including the divestiture of Chrome. The intention behind this drastic measure is to reduce Google’s control over the market and foster competition. The implications of such a move could significantly reshape the browser landscape, opening avenues for rival firms and potentially benefitting consumers with more options and diversity in browser capabilities.
Google’s Response and the Future Direction
Reaction to DOJ Proposals
Google has vehemently criticized the DOJ’s proposals, characterizing them as "staggering" and "extreme." The company insists that such actions could jeopardize American innovation and technology leadership. Google plans to present its own recommendations to the court in the coming months, positioning itself to defend its business model and market presence.
Chrome’s Future in a Competitive Landscape
As the legal proceedings unfold, the future of Chrome hangs in the balance. If divestiture becomes reality, it could not only fracture Google’s ecosystem but also introduce a wave of new players into the market. This scenario could lead to rapid advancements in browser technology, as competition typically accelerates innovation.
By examining Chrome’s remarkable growth and the current regulatory landscape, it becomes evident that the evolution of browsers is inextricably linked to broader technological trends and regulatory actions. As Chrome continues to navigate its future amidst challenges, users will observe significant transformations in how they experience the internet.