The State of Endangered Species: A Closing Look at Threatened Biodiversity
The plight of endangered species is a pressing concern for conservationists and environmentalists around the globe. As of 2024, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) reports that nearly 18,000 species are currently threatened with extinction. This blog post delves into the specifics of these numbers, examining various animal classes and the unique threats they face in today’s rapidly changing ecosystems.
Overview of Endangered Species
The Current Crisis
The staggering statistic from the IUCN highlights a growing biodiversity crisis. Almost 18,000 species are on the brink, categorized as critically endangered, endangered, or vulnerable. This number reflects a significant challenge in the realm of wildlife conservation and raises alarms about the future health of ecosystems worldwide.
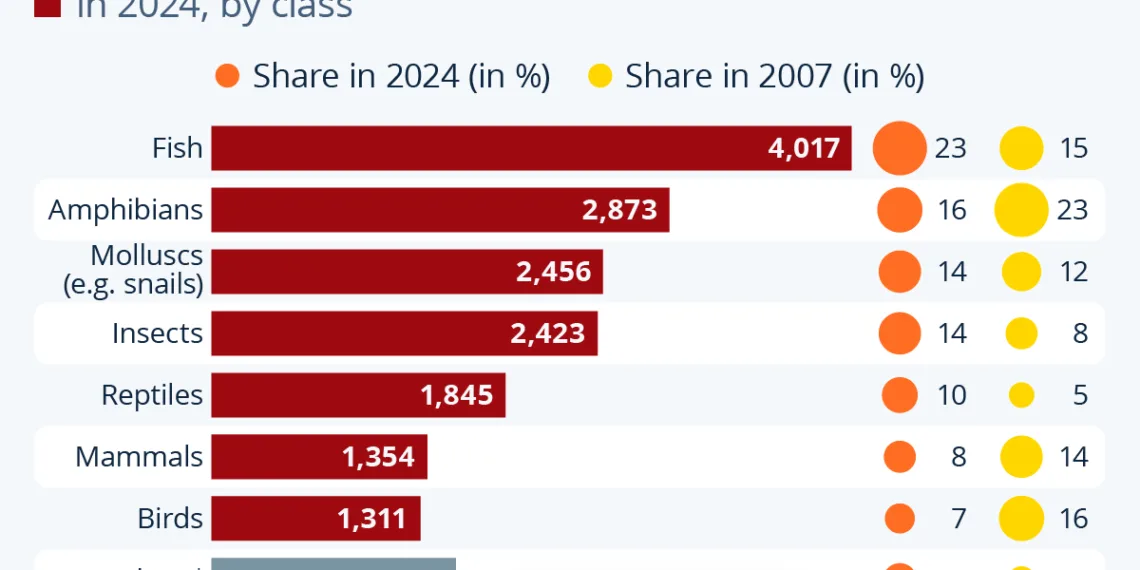
Breakdown of Threatened Species by Class
While most discussions center around charismatic megafauna, such as tigers and orangutans, a detailed analysis reveals that the share of threatened mammals constitutes only about 8% of all endangered species. This analysis uncovers a larger and more complex picture of endangerment, where various animal classes face increasing threats.
The Dominance of Fish and Insects
A Shifting Landscape
Contrary to the traditional focus on mammals, recent data indicate that fish are becoming a significant portion of endangered species, with nearly one in four endangered species being fish. Alongside them, insects have also come to the forefront, representing another area of concern in biodiversity reduction.
Factors Contributing to Their Endangerment
The endangerment of fish and insects is well documented. Overfishing has led to significant population declines in various aquatic species, while pesticide use in agriculture has severely impacted insect populations. Monoculture farming practices further exacerbate the challenges faced by these critical groups, disrupting their natural habitats and food sources.
Understanding the Threats to Reptiles and Molluscs
Reptiles: Vulnerable and Overlooked
Often overshadowed by mammals and birds, reptiles are experiencing a substantial increase in endangerment concerns. Many reptiles thrive in rainforest habitats, making them particularly vulnerable to deforestation. Clearing forests for agriculture or development leads to habitat loss, which drastically impacts these species. Additionally, reptiles are sensitive to environmental changes, and climate change poses a significant threat to their survival.
Molluscs: The Silent Crisis
Molluscs, a diverse group that includes snails, slugs, mussels, and squid, also face rising threats, particularly land and freshwater species. Habitat destruction is a primary concern for many of these creatures, often exacerbated by the introduction of invasive species that challenge native populations. According to research from the American Institute of Biological Sciences, many mollusc species are facing declines as their environments become less hospitable.
The Role of Conservation Efforts
The Importance of Awareness and Action
The continued endangerment of diverse species creates a dire need for robust conservation efforts. Increased awareness and understanding of the specific threats faced by various groups can catalyze more effective action plans that prioritize both protection and habitat restoration.
Collaborative Conservation Strategies
Involving local communities, governments, and international organizations is essential to ensuring the survival of threatened species. Implementing sustainable practices in agriculture, fishing, and land use can pave the way for more resilient ecosystems. Engaging the public in conservation initiatives can also foster a sense of stewardship over wildlife and natural habitats.
Future Directions in Biodiversity Conservation
As we look toward the future, the challenge of conserving endangered species will require innovative approaches. Adopting technology in monitoring populations and restoring habitats, alongside traditional conservation strategies, could enhance our efforts to address biodiversity loss on a global scale.
Exploring these aspects of endangered species highlights the complexity and urgency of preserving our planet’s biodiversity. With awareness and actionable strategies, the hope remains that we can reverse trends of endangerment and foster a thriving natural world.