Understanding EU Migration: The Role of Irregular Entries
Migration within the European Union has been a topic of extensive discussion, particularly in light of recent political narratives. It’s important to examine the factual landscape of migration, especially concerning the notions of irregular migration versus legal migration. The statistics speak for themselves, revealing a more complex picture than often portrayed.
The Current Landscape of Migration in the EU
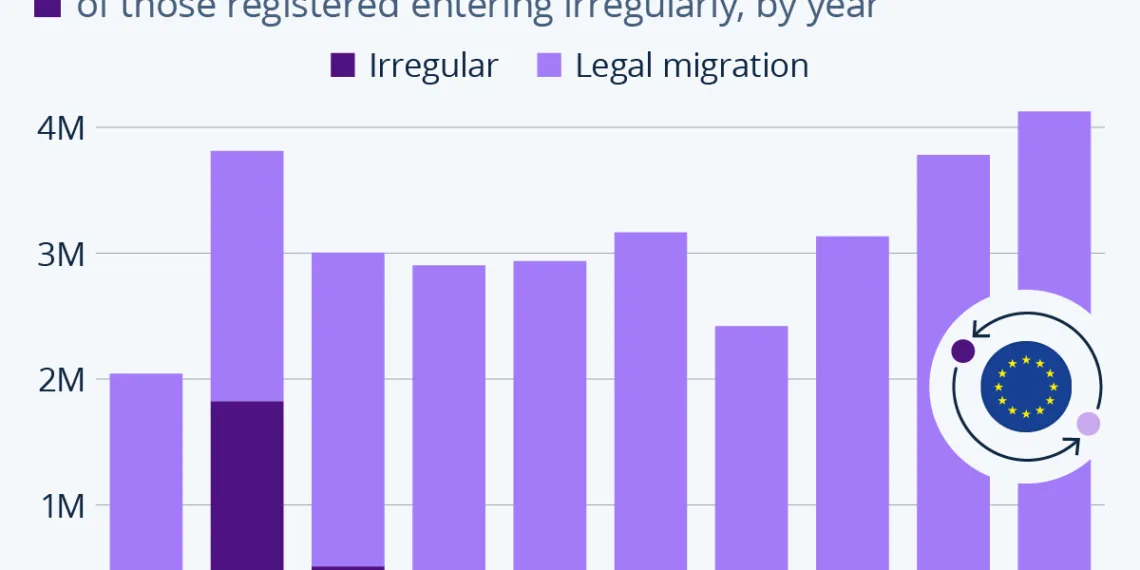
According to Eurostat data, the migration landscape in the EU saw significant movement in 2023, with approximately 4.1 million individuals migrating to the region. This figure underscores the dynamic nature of migration and the various factors driving people to seek opportunities within the EU.
Legal vs. Irregular Migration
A key aspect of this migration is the distinction between legal and irregular migrants. In 2023, less than nine percent of those who migrated were classified as irregular migrants. This statistic serves to highlight that the overwhelming majority of individuals moving to the EU are doing so through legal channels.
- Legal Migration: This category encompasses those who enter the EU with visas, work permits, and other formal pathways that align with immigration regulations.
- Irregular Migration: This involves individuals who enter the EU without proper documentation or who overstay their visas. While a matter of public concern, irregular migration constitutes only a small fraction of total migration flows.
Historical Context of Irregular Migration
To understand the significance of the current data, it is helpful to look back at trends in migration. The year 2015 marked a turning point in Europe’s migration policy, characterized by a notable surge in irregular migration, which led to widespread political and social debates.
The Peak of Irregular Migration
During the height of the migration crisis in 2015, irregular migrant arrivals reached unprecedented levels:
- Volume: The influx of individuals seeking asylum and a better life overwhelmed many EU nations, leading to a scramble for effective policy responses.
- Policy Implications: The crisis prompted the EU to rethink its approach to immigration, culminating in stricter border controls and collaborative efforts among member states to manage migration flows.
Current Trends in Migrant Arrivals
Fast forward to 2023, and the dynamics of migration have changed significantly. Last year’s surge in migrant numbers, driven primarily by legal avenues, illustrates a shift in patterns.
Analyzing the Numbers
- Legal Migrant Dominance: The latest data reveals that the spike in arrivals is almost entirely due to individuals migrating through established legal routes rather than an increase in irregular entries.
- Comparative Analysis: Current irregular migration figures are substantially lower than the peak levels recorded in 2015, indicating that the EU has made strides in managing and regulating migration flows more effectively.
Political Perspectives on Migration
Despite the data indicating a relatively low percentage of irregular migrants, political discourse around migration remains fraught with differing opinions. Politicians express varying beliefs about the implications of migration, often fueling public sentiment and policy decisions.
The Role of Rhetoric
The narratives surrounding migration can significantly influence public perception. For some politicians, emphasizing irregular migration serves to evoke concerns about security, social services, and the strain on national resources.
- Debates and Policies: As these narratives unfold, they shape legislative actions aimed at tightening immigration controls or, conversely, supporting humanitarian efforts to assist migrants.
Conclusion (not included as per instruction)
To explore further, continue examining how migration dynamics evolve with policy changes, economic conditions, and global events impacting migration flows into the EU. This complex web reflects not only statistical data but also the human stories and experiences that lie behind the numbers.