Understanding Child Marriage: A Global Issue
Child marriage is a significant and often overlooked violation of human rights, deeply rooted in cultural, social, and economic factors. It disproportionately affects girls, curtailing their rights and opportunities. The implications of this practice extend far beyond the individual, impacting communities, economies, and societies at large.
The Importance of Consent
According to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the right to "free and full" consent is paramount in marriage. Consent cannot be considered genuine if one party is too young to understand the implications of this lifelong commitment. UNICEF highlights that child marriage violates this principle, leading to detrimental effects on young girls’ lives.
Consequences of Child Marriage
Child marriage often results in severe consequences that can alter a girl’s life trajectory. The repercussions include:
- Teen Pregnancy: Early marriages frequently lead to early pregnancies, exposing young girls to health risks and complications that can arise from childbirth at a young age.
- Educational Barriers: Many girls who marry young drop out of school, significantly affecting their educational attainment and future opportunities. The cycle of poverty perpetuates itself as the girls who miss out on education struggle to achieve better futures.
- Social Isolation: Young brides often find themselves isolated from their peers due to marital obligations, contributing to mental health issues and a lack of social support.
Global Statistics and Regional Disparities
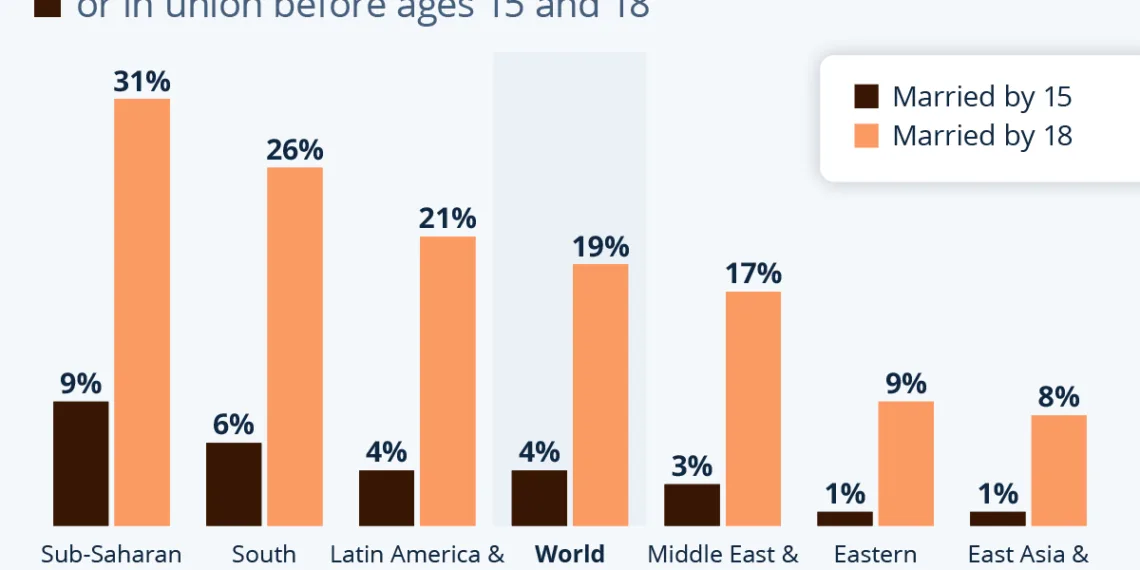
Globally, child marriage continues to be prevalent, with alarming statistics highlighting the need for urgent action. UNICEF estimates that around one in five women aged 20 to 24 were married by the age of 18, while 4% were married before they turned 15.
Regional Summary
-
Sub-Saharan Africa: This region exhibits one of the highest rates of child marriage. Approximately one in three girls are married or enter cohabitation before they reach 18, with 9% of women aged 20 to 24 having entered such unions before the age of 15.
-
South Asia: One in four young women in this region were married by the age of 15, reflecting deep-rooted cultural practices and economic struggles tied to early marriages.
ADVERTISEMENT - Latin America and the Caribbean: The prevalence here is one in five young women entering marriage before turning 18, indicating a concerning trend that mirrors those seen in other regions.
Defining Child Marriage
Child marriage encompasses both formal marriages and informal unions. Many young girls may live with a partner without a legally recognized marriage, often due to cultural practices and legal restrictions that prevent formal unions. This ambiguity complicates efforts to combat the issue, as the nuances of informal unions may not be adequately addressed in legislation.
The Underlying Causes of Child Marriage
Understanding why child marriage persists is essential for formulating effective interventions. Key factors include:
- Poverty: Families often feel compelled to marry off daughters at an early age as a strategy for financial security or to reduce economic burdens.
- Education: Limited access to education perpetuates the cycle of child marriage; without education, girls are often viewed as less valuable and are more likely to be wed early.
- Cultural Norms: In many societies, cultural practices dictate the timing of marriage, disregarding the voice and choices of young women.
Addressing Child Marriage: A Multifaceted Approach
To effectively combat child marriage, a comprehensive and multi-layered approach is necessary. Efforts should focus on:
- Education: Improving access to and the quality of education for girls can significantly reduce the incidence of child marriage.
- Economic Empowerment: Programs aimed at empowering families economically can reduce the financial pressures that lead to early marriages.
- Legal Frameworks: Strengthening laws and regulations against child marriage, as well as ensuring enforcement, is critical to protecting young girls’ rights.
The Role of Communities and Governments
Communities and governments play a vital role in ending child marriage. Awareness campaigns can educate communities about the negative repercussions of child marriage, while government initiatives can provide the necessary resources and legal support to protect young girls.
Conclusion of Child Marriage Perspectives
Child marriage remains one of the pressing human rights violations of our time, deeply intertwined with the broader issues of poverty, education, and cultural expectations. Addressing this complex issue requires concerted efforts and commitment from all sectors of society to create an environment where young girls can thrive, free from the harms associated with early marriage.