The Growing Crisis of Water Conflicts Worldwide
In an era where climate change and increasing population pressures heighten competition for natural resources, water conflicts have come to the forefront as a significant global issue. Recent data indicates that these conflicts are not just an outlier but are on the rise, suggesting a dire situation that warrants urgent attention.
Statistics on Water Conflicts
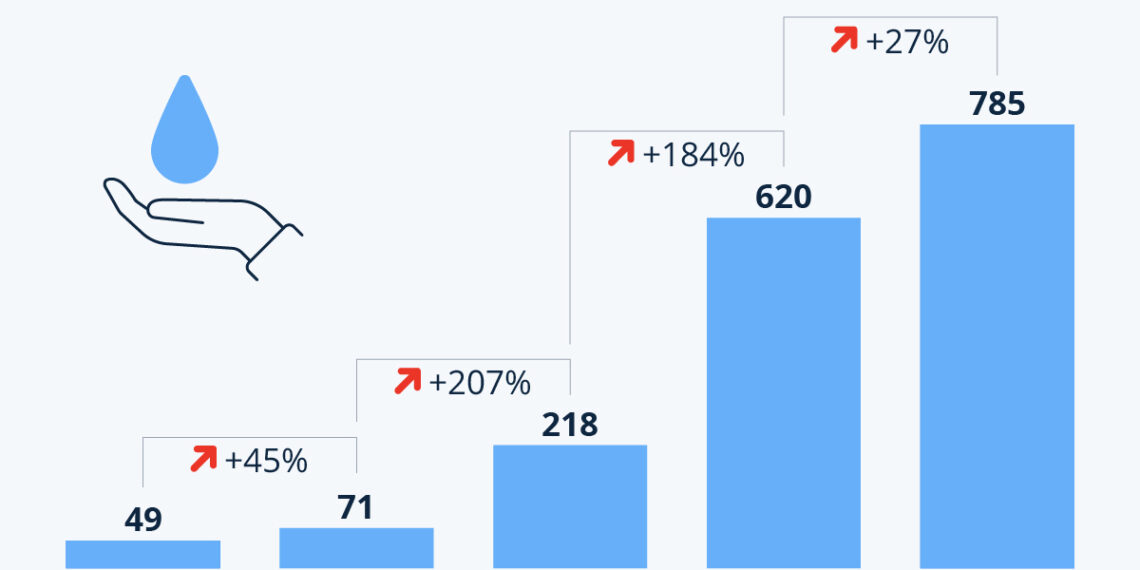
According to a report by the Pacific Institute, there have been 785 recorded water-related conflicts globally in the first four years of the current decade alone. This figure represents a staggering 27% increase compared to the entire decade from 2010 to 2019, which recorded 620 events. Such a rapid ascent in the frequency of these conflicts sends a clear signal that the struggle for control over water resources is intensifying dramatically.
Categories of Water Conflicts
Water conflicts can be divided into three main categories, based on their nature and the role that water plays in instigating violence. Understanding these categories is crucial for forming effective strategies to address the underlying issues.
1. Casualty Conflicts
The first category, referred to as "casualty," encompasses situations where water resources or systems become targets of violence—either intentionally or accidentally. This might involve attacks on infrastructure such as dams, reservoirs, or pipelines, which can disrupt access to water for communities and lead to dire humanitarian crises. The ramifications extend beyond immediate physical harm, as these attacks can erode trust among communities and escalate tensions.
2. Weaponization of Water
The second category involves situations where water resources or infrastructure are utilized as tools of war—known as the "weapon" category. This can manifest in various forms, such as cutting off water supplies to civilian populations during conflicts to demoralize or displace them. Such strategies highlight not only the strategic importance of water but also the profound ethical implications of its use in warfare.
3. Trigger Conflicts
Lastly, the "trigger" category includes conflicts that arise directly from disputes over control of water resources. These may be fueled by factors such as economic access, disputes over rights to water sources, or the effects of water scarcity exacerbated by climate change. As regions experience drought or diminishing water supplies, competition for these vital resources often leads to violent confrontations.
The Escalating Importance of Water Resources
With the human population expected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, the demand for clean and accessible water will only grow. Additionally, climate change is anticipated to further strain water sources due to erratic weather patterns and prolonged droughts. This scenario underscores the importance of proactive measures in water governance and conflict resolution.
Case Studies and Recent Events
Recent case studies from regions like the Middle East and parts of Africa illustrate how water conflicts can quickly escalate into broader geopolitical crises. In some areas, existing tensions over territory and governance have been compounded by competing claims over water sources, leading to violent clashes that threaten regional stability.
Addressing the Issue: Potential Solutions
While the issue of water conflict is complex, solutions exist that can mitigate its impact. Sustainable management of water resources, investment in technology to improve water efficiency and distribution, and international cooperation on shared water systems are vital strategies for reducing the risks of conflict. Additionally, education and public awareness campaigns can empower communities to manage their water resources effectively, fostering a culture of conservation and collaboration rather than competition.
As the frequency of water conflicts continues to rise, it is evident that complacency is not an option. The time for action is now, and understanding the underlying causes and dynamics of these conflicts is essential for creating a more sustainable and peaceful future.