A Total Lunar Eclipse is happening right now, an astronomical phenomenon that started yesterday evening and will persist into today.
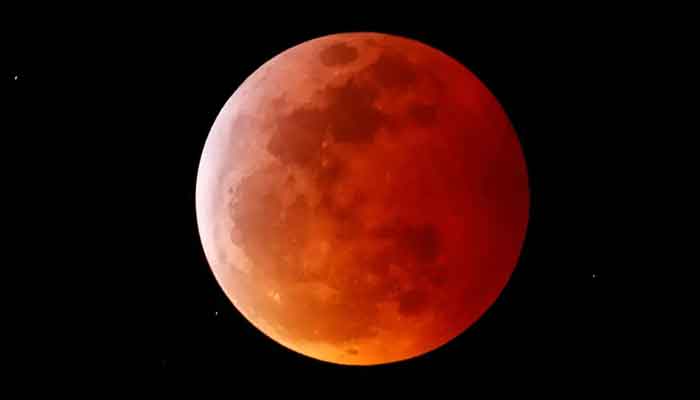
The Moon is illuminated in a striking, coppery-red color, visible from locations across the Western Hemisphere, as reported by Al Jazeera.
It’s important to understand that a lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth is positioned directly between the Sun and the Moon. This alignment blocks sunlight and casts the Earth’s shadow onto the Moon’s surface.
What Causes the Moon to Appear Red During an Eclipse?
During a Total Lunar Eclipse, the Moon takes on a red or orange hue.
This occurs because the only sunlight that reaches the Moon must first pass through the Earth’s atmosphere.
As it travels through, the sunlight interacts with dust particles, water droplets, and atmospheric gases.
A phenomenon known as Rayleigh scattering is also significant here.
This process means that colors of light with longer wavelengths, like red, scatter less and can travel through the atmosphere to reach the Moon, while colors with shorter wavelengths scatter more and do not reach the Moon.
As anyone who has observed a rainbow or played with a prism knows, sunlight comprises a spectrum of colors, from violet (the shortest wavelength) to red (the longest wavelength).
This scattering effect results in the red light that reaches the Moon being reflected off its surface.
While Total Lunar Eclipses are not everyday occurrences, they do not happen too infrequently either, with several occurring each decade.