Select Language:
The Economic and Environmental Impact of China’s Real Estate Sector on Carbon Emissions
China, the world’s largest emitter of carbon dioxide (CO₂), is undergoing a significant transformation in its economic landscape, particularly in its real estate sector. As of March 2024, there has been a notable shift in the nation’s carbon emission trajectory, largely influenced by the ongoing real estate slump. This blog dives deep into the interplay between China’s real estate crisis and its impact on CO₂ emissions.
Understanding China’s Real Estate Crisis
Background of the Real Estate Market
China’s real estate market has long been a cornerstone of its economic growth, contributing substantially to GDP. However, the sector has faced severe challenges in recent years, characterized by a collapse in housing prices, increased defaults from developers, and a significant decrease in construction activities. These economic struggles have sparked intense discussion about the future of real estate in China and its broader implications for the economy.
Effects on Construction and Building Materials
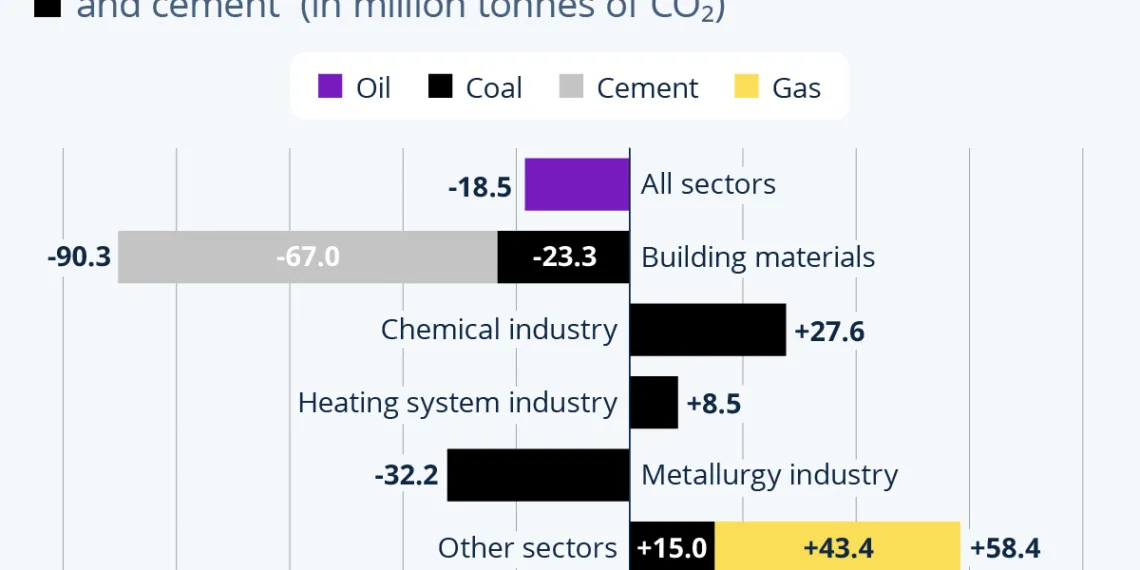
The real estate downturn has led to a sharp decline in demand for new construction projects. With fewer buildings being erected, there has been a notable reduction in the need for building materials. This downturn is crucial because the production and transportation of building materials like cement and steel are significant contributors to carbon emissions.
CO₂ Emissions: A Year-on-Year Analysis
Changes in CO₂ Emissions from the Construction Sector
According to an analysis by Lauri Myllyvirta, published on Carbon Brief, the slump in the real estate sector contributed to a remarkable decrease in CO₂ emissions. Between March and December 2024, there was a drop of approximately 90.3 million tonnes of CO₂ emissions from the building materials sector alone. This decline is evidence of how interconnected the real estate market and industrial emissions are.
The Broader Emission Landscape in 2024
While the decline in emissions from the construction sector is significant, it is essential to note that China’s overall CO₂ emissions did not experience a downward trend in 2024. This phenomenon is primarily attributed to a surge in energy demand as the country began to emerge from the strict zero-COVID policies.
The Balancing Act of Economic Growth and Emissions
Post-Pandemic Energy Demand
China’s re-opening from its strict COVID-19 restrictions has led to a rapid recovery in energy consumption. Industries have resumed operations at full capacity, and the increased demand for electricity has overshadowed the emissions reductions from the construction sector. Consequently, while one sector sees a decrease in emissions, another offsets these reductions through heightened energy demands.
Future Implications for Policy and Sustainability
The contrasting trends of reduced emissions in the construction sector and increased energy demand highlight a crucial challenge for policymakers. It brings forth discussions on how to balance economic recovery while adhering to sustainable practices. As China navigates this complex situation, the interplay between sectoral performance and emissions will remain a focal point in pursuing climate goals.
Conclusion
This article will be concluded in additional content, focusing on the future pathways for China’s emission strategies and the potential lessons that can be learned from the current crisis.